BANKING & FINANCE
- The banking and finance sector in India is highly regulated and complex, playing a crucial role in the country’s economy. The legal framework governing this sector is extensive and designed to ensure stability, transparency, and consumer protection.
Regulatory Framework
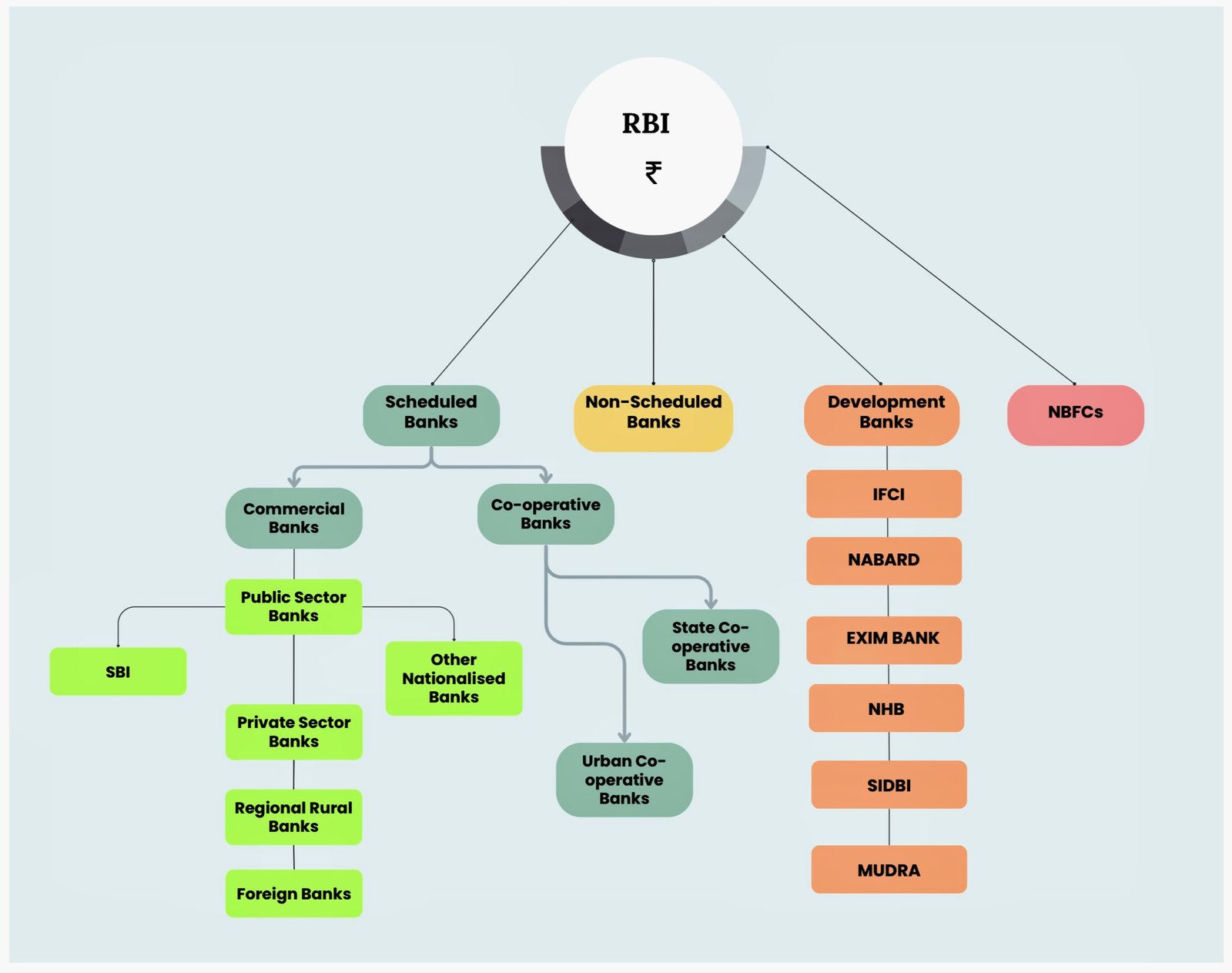
- Reserve Bank of India (RBI): The RBI is the central regulatory authority for banking in India. It oversees the functioning of commercial banks, non-banking financial companies (NBFCs), and other financial institutions. The RBI is responsible for monetary policy, licensing of banks, regulation of interest rates, and ensuring the financial system’s stability.
- Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI): SEBI regulates the securities market, including the issuance and trading of securities, mutual funds, and the activities of financial intermediaries.
- Ministry of Finance: The Ministry of Finance plays a key role in shaping financial policies, including those related to banking, insurance, and capital markets.
- National Bank for Agriculture and Rural Development (NABARD): NABARD is a statutory body established to promote and finance agriculture and rural development in India. Its primary focus is on improving the economic conditions of rural areas through financial assistance and infrastructure development.
- Small Industries Development Bank of India (SIDBI): SIDBI is a government-owned financial institution that supports the growth and development of small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) by providing financial assistance for setting up new businesses, expanding existing ones, and modernizing technology.
- Export-Import Bank of India (EXIM Bank): EXIM Bank is a government-owned financial institution that provides comprehensive financial assistance to Indian exporters and importers, facilitating international trade and promoting India’s export-oriented industries.
- Insurance Regulatory and Development Authority of India (IRDAI): IRDAI regulates the insurance sector, ensuring compliance with laws and protecting policyholders’ interests.
Key Laws and Regulations
- Banking Regulation Act, 1949: This act governs the operations of commercial banks, including their licensing, capital requirements, and management. It also provides for the regulation of banking companies by the RBI.
- Reserve Bank of India Act, 1934: This act established the RBI and defines its powers, including the regulation of monetary policy, currency issuance, and supervision of banks and financial institutions.
- Negotiable Instruments Act, 1881: This act governs the use of negotiable instruments like cheques, promissory notes, and bills of exchange, including their negotiation, transfer, and liability.
- Payment and Settlement Systems Act, 2007: This Act empowers the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) to regulate and oversee payment systems, including electronic payments, cheques, and other financial transactions.
- Companies Act, 2013: This act regulates the incorporation, management, and dissolution of companies, including those in the banking and finance sector. It also governs corporate governance, mergers, and acquisitions.
- SARFAESI Act, 2002: The Securitization and Reconstruction of Financial Assets and Enforcement of Security Interest (SARFAESI) Act empowers banks and financial institutions to recover non-performing assets (NPAs) without court intervention.
- National Housing Bank Act, 1987: This Act established the National Housing Bank (NHB) in India. The National Housing Bank (NHB) promotes housing finance in India by providing financial assistance to Housing Finance Companies, regulating them, promoting affordable housing, developing a secondary market for housing loan securities, and conducting research and development.
- Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code (IBC), 2016: The IBC provides a time-bound framework for resolving insolvency and bankruptcy cases, applicable to individuals, companies, and partnership firms.
- Foreign Exchange Management Act (FEMA), 1999: FEMA governs foreign exchange transactions, cross-border trade, and investments in India, and is critical for banks dealing with international transactions.
- Prevention of Money Laundering Act (PMLA), 2002: This act aims to combat money laundering and requires banks and financial institutions to implement anti-money laundering (AML) measures.
Required Services in Banking and Finance
- Advisory Services: Legal advisors provide guidance on regulatory compliance, structuring of financial products, and risk management. They help banks and financial institutions navigate complex legal environments and avoid penalties.
- Comprehensive Legal Support for Transactions: Legal professionals assist in drafting, reviewing, and negotiating contracts related to loans, securities, mergers, and acquisitions, ensuring that all agreements are legally sound and enforceable.
- Litigation and Dispute Resolution: Lawyers represent banks and financial institutions in litigation related to loan defaults, recovery proceedings, and other disputes. They also provide arbitration and mediation services to resolve conflicts.
- Due Diligence: Conducting legal due diligence is crucial for transactions involving mergers, acquisitions, or the issuance of securities. This process helps identify potential legal risks and liabilities.
- Compliance Audits: Legal professionals conduct compliance audits to ensure that banks and financial institutions adhere to all applicable laws and regulations, minimizing the risk of legal action and financial loss.

Our Role
Arvind Attorneys is well-equipped to serve the complex legal needs of the banking and finance sector in India. We are committed to providing high-quality, comprehensive legal services tailored to the banking and finance sector’s unique challenges. By leveraging our deep expertise, strategic approach, and client-focused solutions, we help our clients navigate the complex legal landscape, achieve compliance, manage risks, and secure successful outcomes in their business endeavours.